The Vietnamese state apparatus is the organizational system of state agencies that perform the State’s social management function. This is the power apparatus of the State, elected by the people through elections to the People’s Councils at all levels and elected by the People’s Councils. The current Vietnamese state apparatus diagram includes three main systems: state power agencies, state administrative agencies and state judicial agencies.
System of state power agencies
The system of state power agencies includes the National Assembly, the President and People’s Councils at all levels.
Congress
The National Assembly is the highest representative body of the people and the highest state authority in the state government system. The National Assembly exercises constitutional, legislative, and supreme supervision over the activities of the State and the entire socio-political system.
- Mission: Decide on important guidelines and policies of the country; promulgate laws and ordinances; Supervise, question, and approve important decisions of the Government, the Supreme People’s Court, and the Supreme People’s Procuracy; elect the President, Vice President, Chairman of the National Assembly, Vice Chairman of the National Assembly, Standing Committee of the National Assembly, Government, Supreme People’s Court, Supreme People’s Procuracy.
- Powers: Amending and abolishing the constitution; promulgate, amend, and repeal laws and ordinances; issue resolutions on important guidelines and policies of the country; Supervise, question, and approve important decisions of the Government, the Supreme People’s Court, and the Supreme People’s Procuracy; elect the President, Vice President, Chairman of the National Assembly, Vice Chairman of the National Assembly, Standing Committee of the National Assembly, Government, Supreme People’s Court, Supreme People’s Procuracy.
President
The President is the Head of State, the symbol of unity of the entire people, and the supreme representative of the State of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam in foreign relations.
- Duties: Leader of the National Defense and Security Council; On behalf of the state, appoint, dismiss, promote, and demote positions for positions elected by the National Assembly; ratify and promulgate laws of the National Assembly; issue amnesty and special amnesty orders.
- Powers: Order mobilization of all or part of the armed forces; promulgating a state of emergency or a state of war; On behalf of the state, sign international documents, treaties and treaties approved by the National Assembly; Adjust the organization of the Government; Sign and approve the law-making project; decide to establish, dissolve, merge, and divide administrative units; decide to appoint and dismiss commanders of military zones, heads of military zone-level agencies, commanders and heads of agencies equivalent to military zones; Approve the list of staff appointments submitted by the Government.
People’s Councils at all levels
The People’s Council is a local state power agency, elected by the people. The People’s Council decides on important local policies and guidelines, supervises the activities of the People’s Committee, other local agencies and citizens.
- Tasks: Issue resolutions on important local guidelines and policies; Supervise the implementation of local constitutions, laws and ordinances; elect and dismiss the People’s Committee and positions prescribed by law; Decide on other issues regarding local organization and operations according to the provisions of law.
- Powers: Issue resolutions on important local guidelines and policies; Supervise the implementation of local constitutions, laws and ordinances; elect and dismiss the People’s Committee and positions prescribed by law; Decide on other issues regarding local organization and operations according to the provisions of law.
State administrative agency system

The system of state administrative agencies includes the Government, People’s Committees at all levels, ministries, institutes, councils and equivalents under the Government and People’s Committees at all levels.
Government
The Government is the highest administrative agency of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam, exercising unified executive power throughout the country under the authorization of the National Assembly.
- Tasks: Prepare law projects, resolution projects, state budget estimates; decide on the action program of the Government and organizations under the Government; organize the implementation of resolutions and action programs of the National Assembly and the Government; Manage other activities according to the authority assigned by the National Assembly and the President.
- Powers: Prepare law projects, resolution projects, state budget estimates; decide on the action program of the Government and organizations under the Government; organize the implementation of resolutions and action programs of the National Assembly and the Government; Manage other activities according to the authority assigned by the National Assembly and the President.
People’s Committees at all levels
The People’s Committee is a local administrative agency, elected by the People’s Council. The People’s Committee exercises state administrative powers, implements resolutions of the People’s Council and the work of the Government locally.
- Mission: Organize the implementation of Resolutions of the People’s Council and work of the Government; promulgate specific regulations guiding the implementation of Resolutions of the People’s Council and the work of the Government applied locally; Carry out state management of all aspects of local activities.
- Powers: Organize the implementation of Resolutions of the People’s Council and work of the Government; promulgate specific regulations and guidelines
Executive Committee of the General Assembly of the President of the Republic of Vietnam and the People’s Republic of China for the Current Work in the South of the Government
government and local authorities; Thc is extremely effective in controlling the way governments around the world create new aspects of current practice in their local functions.
Ministry, country, government, civil society and presidential candidate
The Ministry of Justice, Advancement, Institute, Council and equivalent are agencies that assist the Government within the scope of their duties and powers. .These observations are due to the fact that the government has established an establishment, in the organization, the organization has been established.
- The Ministry’s tasks: Construction, construction, and planning of the Government include many legal projects, land recommendations, and decisions of the Government; togethercheck . According to the guidance, instructions, and guidelines for developing units of communes and households, a clear understanding of the structure and organizational principles of the state apparatus is very important to build a sustainable and effective public administration system. fruit.
Organizational Chart of the Vietnamese State Apparatus
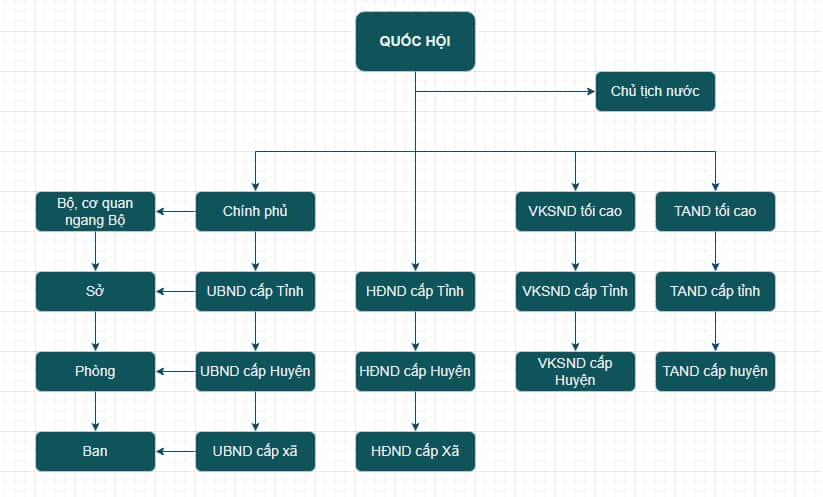
Brief answer to the Vietnamese state apparatus:
- The system of state agencies is organized according to the principle of unity and performs the functions of the State.
- Includes three types of agencies: legislative, executive, and judicial.
- The main agencies in the Vietnamese state apparatus diagram include:
- Congress
- President
- Government
- The People’s Court
- People’s Procuracy
- Local government
Congress
The National Assembly is the highest authority in the Vietnamese state apparatus system. The main role of the National Assembly is to exercise constitutional, legislative and supervisory powers. Below are the main agencies in the National Assembly organizational chart:
National Assembly Standing Committee
- The National Assembly Standing Committee is the highest administrative body of the National Assembly.
- The daily work of the National Assembly is responsible for the National Assembly Standing Committee.
- The National Assembly Standing Committee plays an important role in managing the activities of the National Assembly, preparing for National Assembly sessions and monitoring the implementation of National Assembly resolutions.
Ethnic Committee
- The Committee for Ethnic Minorities is an agency of the National Assembly responsible for supervising and inspecting the implementation of policies and laws on ethnic groups and regions and areas with ethnic minority characteristics.
President
The President is the Head of State, representing the State at home and abroad. The role of the President is not only to represent the nation but also to ensure justice, democracy and integrity of the nation. Below are the details related to the Presidency:
Office of the President
- The Office of the President is a high-level administrative agency, directly under the President, responsible for supporting the President in State management and diplomatic representation activities.
National Security Council
- The National Security Council is the President’s highest advisory body in deciding national security policies and measures.
Government
The Government is the highest administrative agency, performing the functions of leadership, state management and executive power. Below are the main agencies in the Government organizational chart:
Goverment office
- The Government Office is the highest administrative agency, directly under the Government, responsible for supporting the Government in state management and socio-political activities.
Ministries and branches
- Ministries and branches in the Government are administrative agencies under the Government, responsible for managing and operating specialized fields and professions according to the decentralization and assignment of the Government.
The People’s Court
The People’s Court is the agency that adjudicates and resolves cases according to the provisions of law. The role of the People’s Court is to protect the legal rights of citizens and society, ensuring fairness and transparency in the law. Below are the details related to the People’s Court agency:
Supreme Court
- The Supreme Court is the supreme agency in the people’s court system, responsible for resolving important, complex issues that have a national scope or require the highest direction from the Supreme Court.
Lower People’s Court
- The lower-level People’s Court is the request agency of the level, responsible for resolving cases according to its authority, ensuring fairness, speed and transparency according to the provisions of law.
People’s Procuracy
The People’s Procuracy is a legal supervision agency, performing the function of state prosecution. The People’s Procuracy is responsible for inspecting and supervising law enforcement and protecting the rights of citizens and society. Below are the details related to the People’s Procuracy agency:
People’s Procuratorate of the Supreme
- The Supreme People’s Procuracy is the highest agency in the People’s Procuracy system, responsible for inspecting and supervising law enforcement at the national level, protecting the rights of citizens and society. .
Local People’s Procuracy
- The local People’s Procuracy is responsible for inspecting and supervising local law enforcement and protecting the rights of citizens and society in accordance with the law.
Local government
Local government is a local state management agency, responsible for performing administrative functions, building and developing the locality. Below are the details related to Local Government agencies:
People’s Assembly
- The People’s Council is a local power agency, elected by voters, responsible for deciding and supervising important local issues in accordance with the law.
People’s Committee
- The People’s Committee is a local administrative agency, subject to the direction of the People’s Council, implementing the People’s Council’s resolutions, managing administrative, economic and social fields according to assigned authority. .
Principles of Organization of the Vietnamese State Apparatus
Peer control:
- Assignment and mutual inspection between legislative, executive, and judicial agencies.
Vertical control:
- The people control state agencies.
- The central government controls localities through decentralization and decentralization of power.
Conclude
Above is an overview of the current Vietnamese state apparatus diagram. Understanding the structure and organizational principles of the state apparatus not only helps us understand the state management system but also assists in promoting the country’s sustainable development. Hopefully the above information will provide readers with an overview and detail of the Vietnamese state apparatus system and the role of each agency in it.
If you have any questions, please send to Hotline number 09633458xxx or email address tuyengiaothudo.vn@gmail.com for answers. Best regards!
Tuyên bố miễn trừ trách nhiệm: sesua.vn là website tổng hợp kiến thức từ nhiều nguồn,Vui lòng gửi email cho chúng tôi nếu có bất cứ vi phạm bản quyền nào! Xin cám ơn!
- TAND Tối cao giải đáp 07 vướng mắc xét xử liên quan đến hành chính
- 20+ Cách làm tóc dài nhanh, mượt mà từ gốc đến ngọn
- Biển Số Xe 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 40 Ở Tỉnh Nào? Giải Đáp Chi Tiết Về Biển Số Xe Hà Nội
- Nội dung tập sự hành nghề công chứng theo Thông tư 08/2023/TT-BTP
- Quy định về hình thức xử phạt với lỗi thay đổi kết cấu xe?













